Skin Conditions in Newborns: Causes, Symptoms, and Care Tips

These conditions include:
- newborn acne (white acne, milia)
- sweat rash (lat. miliaria)
- toxic erythema of newborns (lat. erythema toxicum neonatorum)
- erythema neonatorum
- mongolian spots
- a stork bite (salmon patch) (lot. nevus simplex)
- de****mation (lot. desqvamatio neonatorum)
- cradle cap
- characteristic white papules (palpable small bumps on the skin)
- the most common localization is in the area of the nose and cheeks
- usually resolves without treatment within 3-4 months


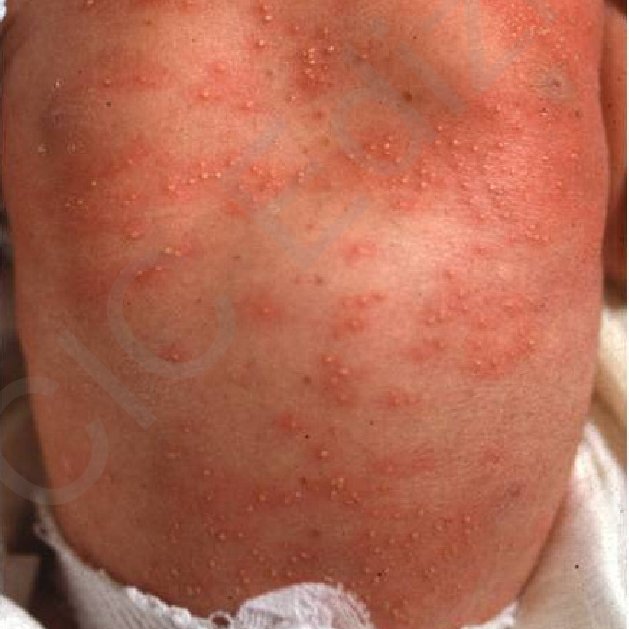
- main manifestation –pink dots
- occurs due to blocked sweat glands, usually due to overheating
- localization: on the forehead, but can also be on the body
- crystalline miliaria – superficial vesicles, 1-2 mm in diameter, no redness
- sweat miliaria – small palpable skin bumps (papules) and pustules (pustules)
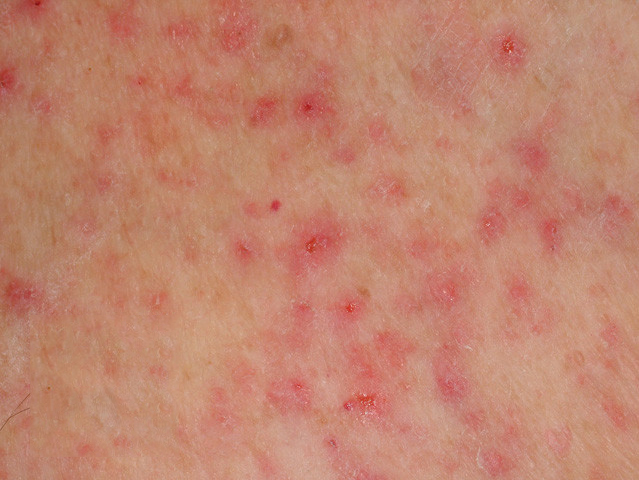
- irregular red spots with a yellowish hard nodule in the center
- formed in the skin of the face, limbs, and body on the 2nd-5th day of life due to the rearrangement of protein metabolism
- resolves spontaneously within 2-3 weeks
- it is a reaction to breast milk proteins, no treatment is required
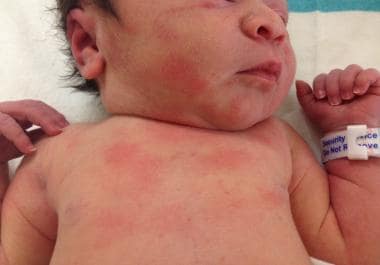
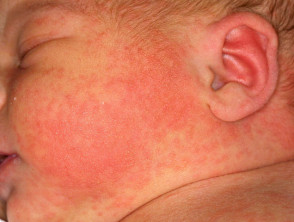
- emerges pink spots
- On the 1st-2nd day of life due to the skin’s reaction to the environment
- disappears on the 4th-7th day
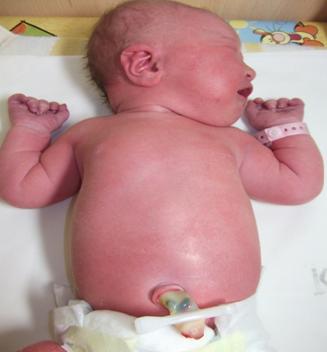
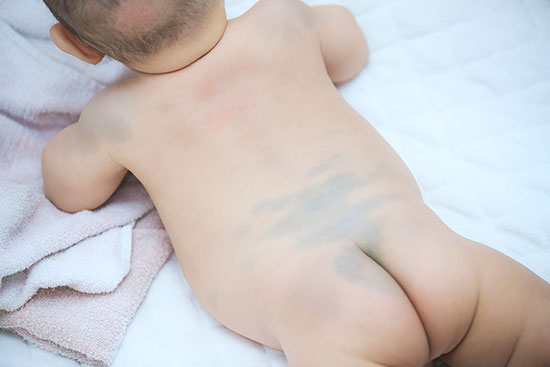
- occurs due to uneven pigment distributiongray-blue spots
- characteristic of 80 percent African, Asian, Indian and Roma newborns
- the most common localization: the skin of the buttocks, may be the torso, limbs
- disappear within weeks or even years
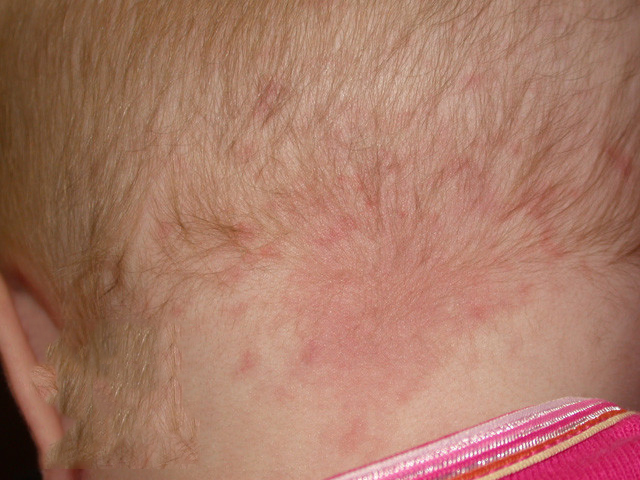
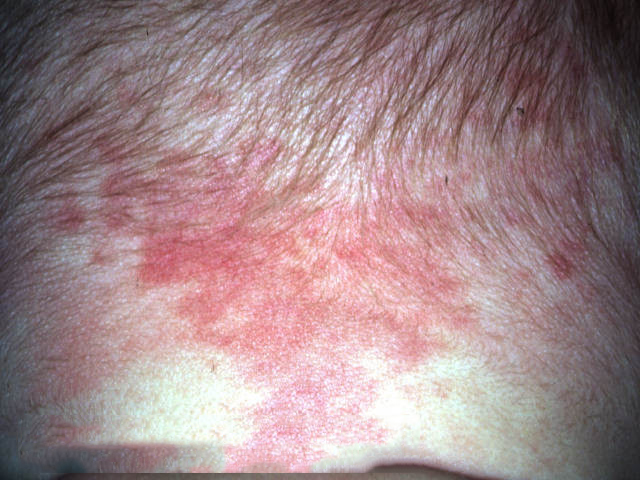
- occurs due to the increased vascular network in the skin pink spots
- usually disappears within 6 months
- localization: most typical in the neck area, less often on the forehead, eyelids
- appears on the 3rd-5th day of life
- characteristic of the skinpeeling, flaking
- in more severe cases, may appear cracks, wounds
- usually resolves on its own
- localization: newborn abdomen, chest area, limbs
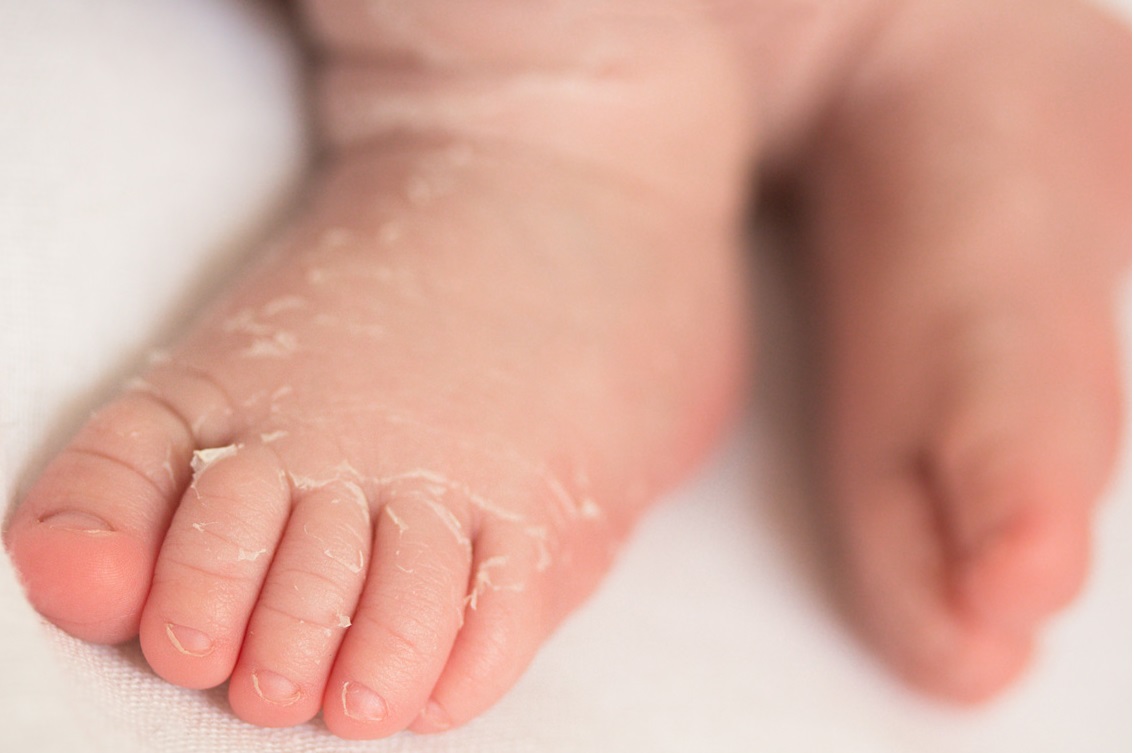

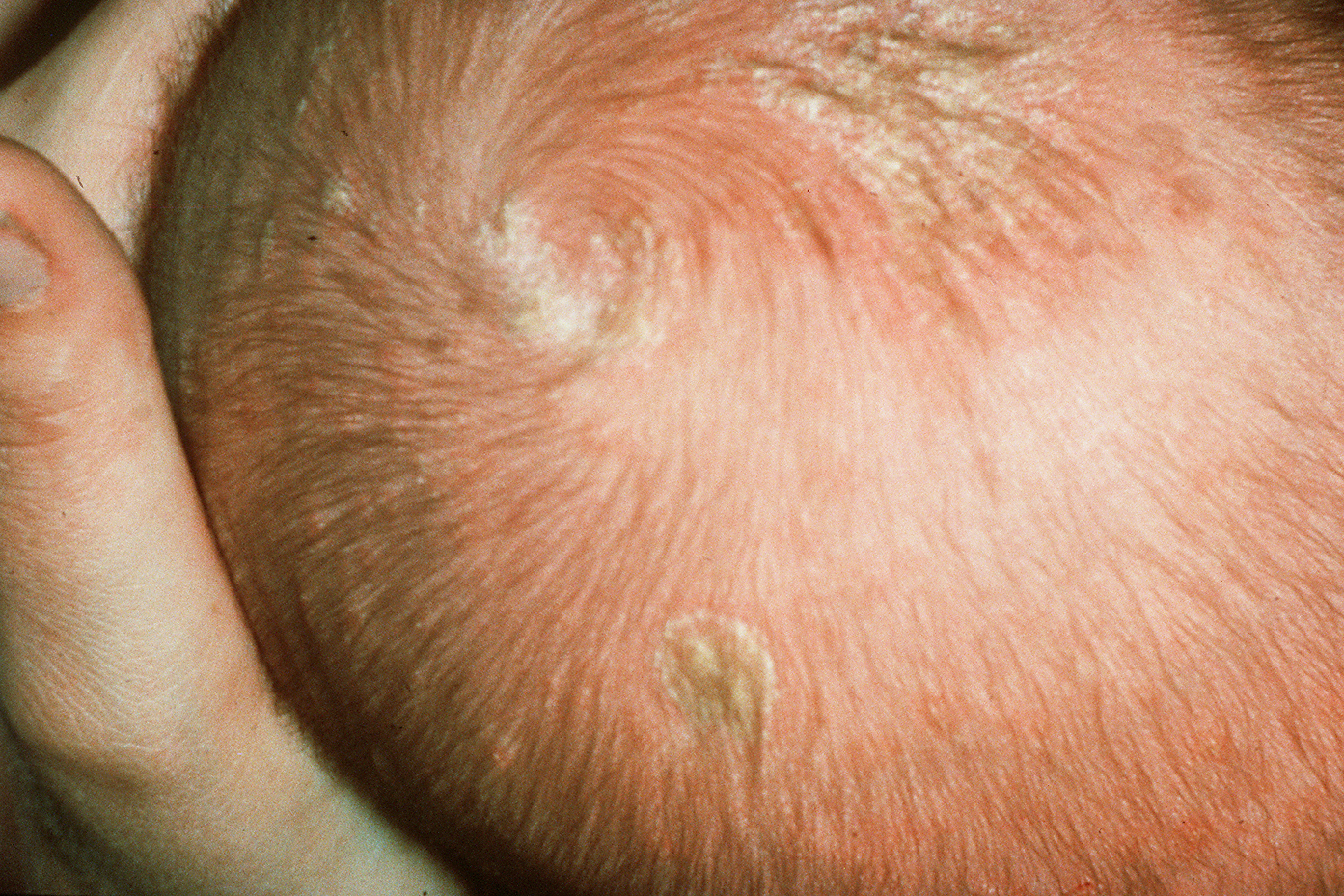
- occurs in the first months of life due to increased activity of sebaceous glands and/or the effects of fungi and bacteria
- characteristic yellowish, scale-like, greasy dandruff
- does not cause itching or pain
- usually resolves on its own within a few weeks or months
- localization: scalp
For the diagnosis of skin conditions in newborns, data from the patient’s examination and the parent’s interview are usually sufficient. In rare cases, a skin biopsy or general examination may be necessary to rule out other possible diseases.
Treatment
All these skin conditions are characterized by the fact that they are a normal reaction of the newborn’s body to changes in the environment, so they usually do not require specific treatment and pass by themselves. It is important to recognize them correctly and not confuse them with conditions requiring treatment. During the consultation, the doctor may prescribe treatment to reduce the symptoms.


Pitted Keratolysis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Pitted keratolysis is a bacterial skin condition affecting the soles of the feet, causing small pits and a strong odor. Treatment includes antibacterial creams and proper foot care to reduce symptoms and improve skin health.
Angular Cheilitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Angular cheilitis is a condition that causes painful cracks and inflammation at the corners of the mouth. It can be treated with moisturizers and antifungal or antibacterial creams to reduce symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Lichen Planus: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes itchy, flat, purplish rashes. Effective treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving skin health to prevent discomfort and flare-ups.





