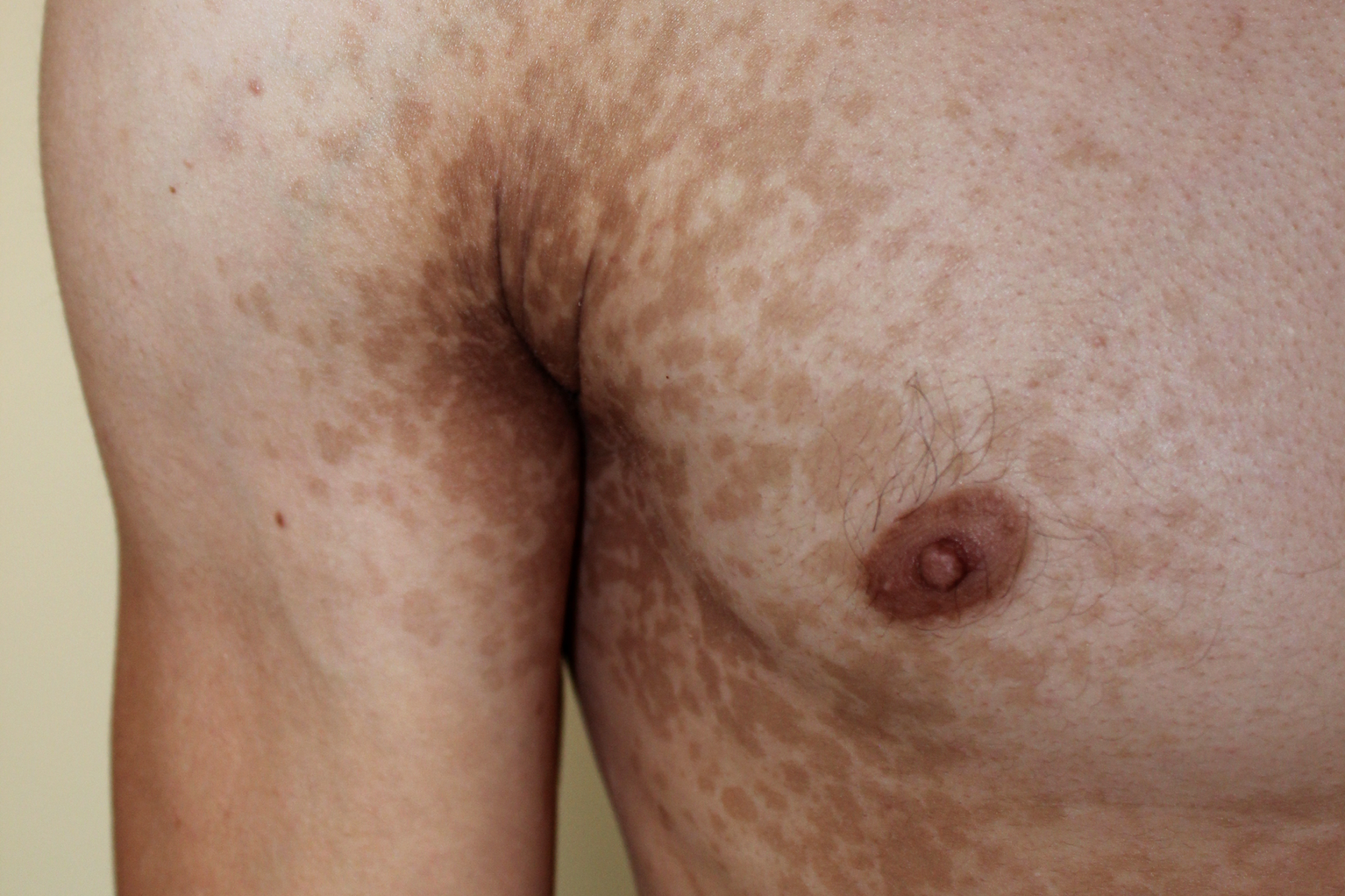
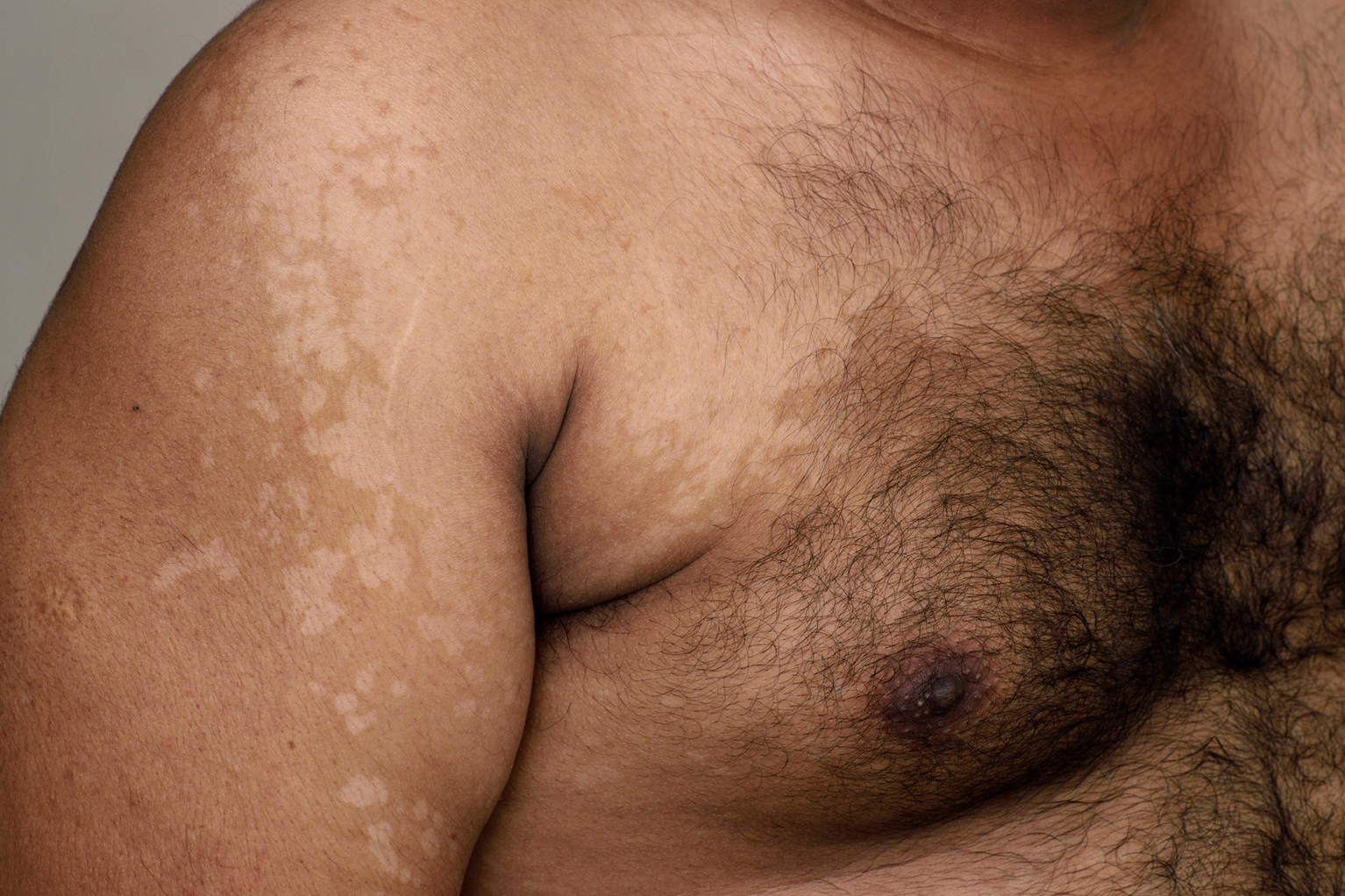
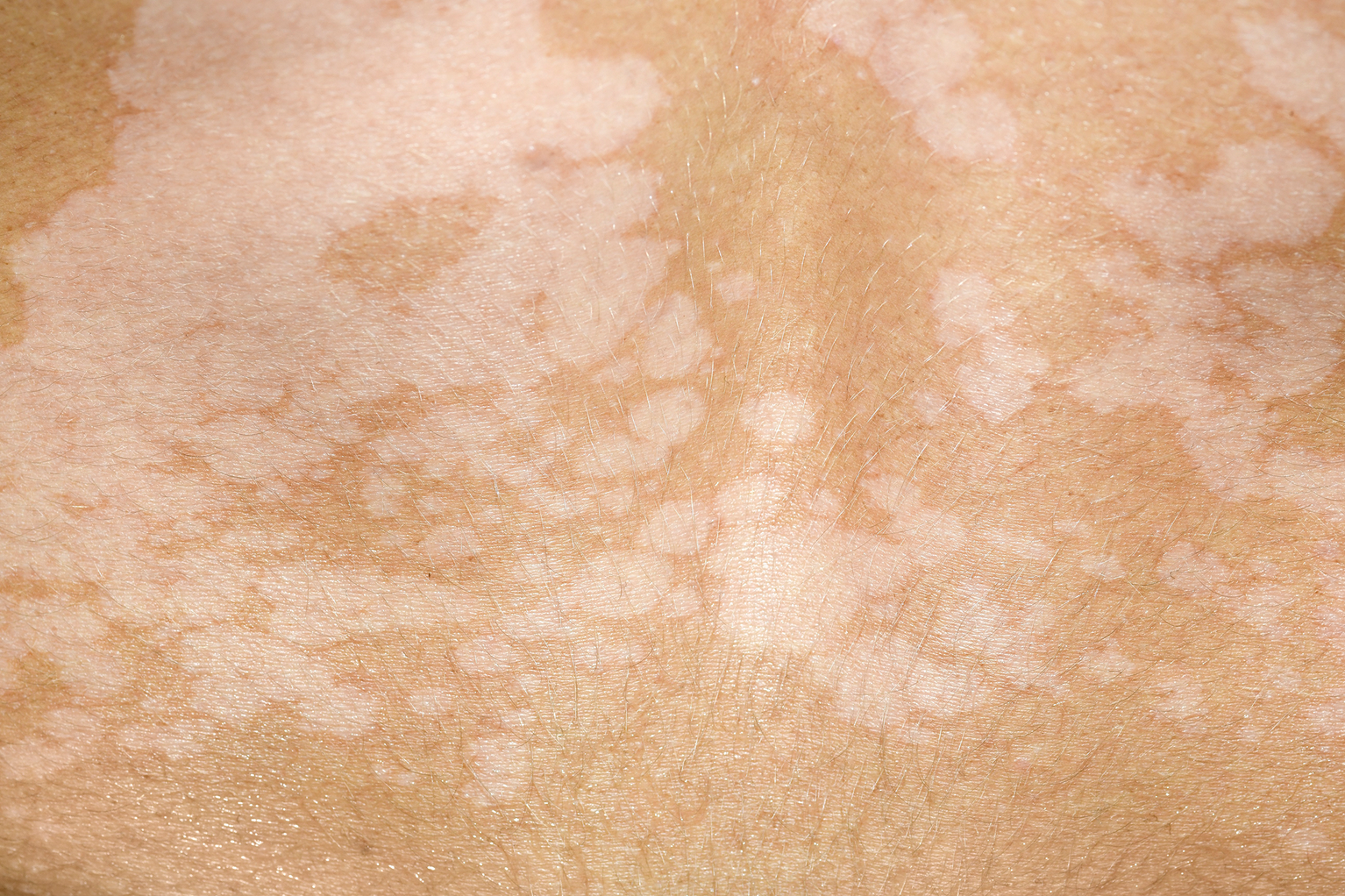
Multi-coloured ringworm

Multi-coloured ringworm is a skin rash caused by a fungus of the Malassezia species, called ‘multi-coloured’ because of the wide range of colours and shades of the rash. About 14 different species of Malassezia fungi can be identified. This is
a normal part of the skin’s microflora, which usually doesn’t cause any discomfort or rashes. The disease is not contagious. It can affect both children and adults.

Clinical signs
When conditions are favourable (humid, warm environment, increased sweating, tight synthetic clothing, weakened immunity due to infection) and the fungus on the skin surface increases, the lesions characteristic of multi-coloured dedermatitis appear:
-
- red, brownish or brown, whitish spots and blotches of various diameters
- affected areas may become scaly
- itching is not severe, more common after warming up
- the rash does not burn after sun exposure and gives the appearance of “mottled” skin
- rashes on the neck, back, chest, abdomen, arms and, less commonly, thighs
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is based on characteristic symptoms and clinical signs. Additional tests may be needed if the disease has been left untreated for a long time, leading to symptoms that could be attributed to other skin diseases. In this case, additional tests are carried out:
-
- inspection with Woodhouse lamp
- dermatoscope examination
- microscopic examination of a scratchy, scaly rash for fungal detection
- in rare cases, a biopsy of a skin graft
Treatment
An antifungal cleanser and an antifungal medication to be applied to the rashes. In the case of a prolonged course of the disease, or if the rash is very widespread or recurs frequently, your doctor may also prescribe oral antifungal drugs.
If you notice rashes typical of multicoloured powdery mildew, you can help yourself with an antifungal cleanser if they are not widespread. If the rash persists, we recommend consulting a dermatovenereologist.

Paraneoplastic dermatological manifestation of gastrointestinal malignancies
rare disorders resulting from the immune system’s response to a cancerous process (neoplasia) in the body. Gastrointestinal neoplasms more often cause paraneoplastic syndromes affecting the skin.
Nail psoriasis
Psoriasis is a form of chronic systemic inflammatory autoimmune disease that mostly affects fingernails and toenails.
Lyme disease
It is contracted when a blood-sucking tick injects intestinal contents containing bacteria into a wound. Untreated Lyme disease can damage not only the skin, but also the internal organs, joints and nervous system.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškės g. 99, Vilnius
+370 671 33323
[email protected]




