Infectious mollusc

The causative agent is Molluscum contagiosum virus, family Poxviridae, a member of the DNA virus group.
Routes of infection:
- through direct contact with the sick person
- through contaminated objects (towels, bed linen, sponges)
- transmission of the virus by the patient to healthy areas of the skin through digging or shaving (autoinoculation)
Risk factors
- young age
- weakened immune response (due to chemotherapy or other similarly acting drugs, certain diseases or conditions)
- diseases affecting the skin barrier (atopic dermatitis)
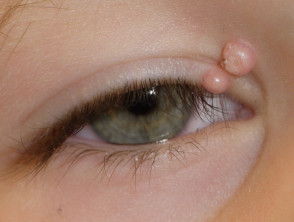

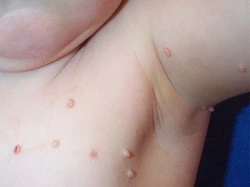

- It usually takes 2 weeks from the time of infection until the first symptoms appear. Less common can occur from 2 weeks to 6 months
- The infection appears as one or more papules (palpable skin bumps) up to 5 mm in size, whitish-brownish, shiny in colour, the central part sunken (umbilication)
- Inside each papule is a white, cheesy substance
- As the ferns die back, they can become inflamed, scabby or scabby within a week or two
- Localisation: skin of the whole body, more often the face, armpits, trunk, underarms, anus and genital area
- Children with atopic dermatitis or other diseases affecting the skin barrier, and immunocompromised individuals, may have more severe symptoms and require a longer period to recover
- After ~6 months characterised by spontaneous resolution of symptoms if the affected person has normal immunity
History and clinical findings are usually sufficient to make the diagnosis. Although not usually necessary, it is useful to have a dermatoscopy if possible.
Treatment and prevention
There is no specific treatment for this viral infection, but it is possible to speed up the recovery process. This may involve topical treatments with certain substances or procedures to remove the skin lesions.
Your doctor can recommend the best treatment method for you.
While the infection is active, the sick person can infect others. To prevent the spread of infection and re-infection, it is useful to take the following preventive measures:
- maintain good hand hygiene
- avoid scratching or shaving
- cover any abrasions with clothing or a waterproof patch
- discard used patches immediately
- not to use other people’s towels, clothes or other items

Paraneoplastic dermatological manifestation of gastrointestinal malignancies
rare disorders resulting from the immune system’s response to a cancerous process (neoplasia) in the body. Gastrointestinal neoplasms more often cause paraneoplastic syndromes affecting the skin.
Nail psoriasis
Psoriasis is a form of chronic systemic inflammatory autoimmune disease that mostly affects fingernails and toenails.
Lyme disease
It is contracted when a blood-sucking tick injects intestinal contents containing bacteria into a wound. Untreated Lyme disease can damage not only the skin, but also the internal organs, joints and nervous system.




