Folliculitis

Risk factors:
Folliculitis can be triggered by certain risk factors. Most can be prevented or reduced by lifestyle changes. These factors include:
-
- carriage of S. aureus in the nasopharynx
- follicular closure (e.g. using inappropriate skincare products)
- sweating
- digging
- taking glucocorticoids (hormones)
- shaving against the direction of hair growth
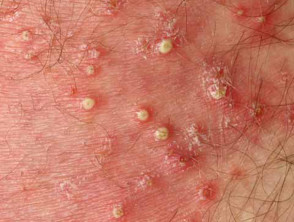
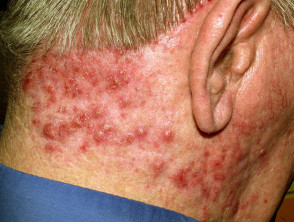
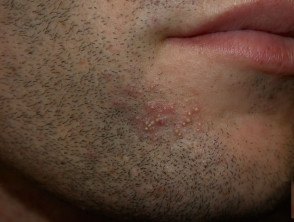
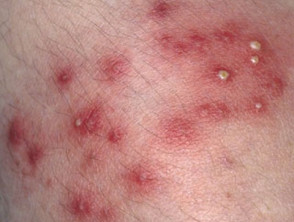
Causes and classification of the disease
Folliculitis can be divided into superficial and deep. Superficial can be infectious or non-infectious.
Infectious :
-
- bacteria: S. aureus, Pseudomonas spp.
- fungi: derma****tes, Malassezia spp., Candida spp.
- Herpes simplex, Varicella zoster
- parasites: Demodex mites
Deep folliculitis is more finely dissected:
-
- furunculus
- sycosis (folliculitis barbae)
- pseudofolliculitis barbae (beard pseudofolliculitis)
- acne keloidalis
Folliculitis is characterised by skin lesions:
- rash: pustules (abscesses) and papules (palpable bumps on the skin)
-
- related to the hair follicle
- may itch
- may be painful
- hypo/hyperpigmentation, scarring of the skin may remain after recovery
- may progress to furuncle, an inflammation of deeper tissues
-
- localisation of lesions: face, beard, scalp, waist, buttocks, legs
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of folliculitis is based on medical history and clinical data. In rare cases, additional tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis, when history and clinical data are insufficient:
- KOH microscopy – for suspected folliculitis caused by fungi or Demodex
- microscopic examination, culture – if bacterial folliculitis is suspected
- PCR – for suspected viral folliculitis
Treatment
Treatment for folliculitis varies depending on the underlying cause. Common approaches include eliminating risk factors and applying general antiseptic solutions.
Specific treatments are tailored based on the type of causative agent:
- For bacterial causes, topical or systemic treatments may be used.
- In cases of a viral origin, localized or widespread antiviral measures might be considered.
- For fungal-related cases, either topical or systemic antifungal approaches can be appropriate.
- When folliculitis is due to parasitic causes, localized or systemic treatments are available.
Advice and prevention
For folliculitis, it is advisable to consult a dermatovenereologist, especially if the rashes are widespread or if the symptoms persist for several days. After the consultation, it is essential to follow exactly the treatment prescribed by your doctor.
To prevent folliculitis it is advisable to:
- avoid tight, chafing clothing
- wash reusable cloth gloves
- avoid shaving or shave carefully, change blades, choose the right tools
- use only clean hot tubs, swimming pools

Psoriasis
A common, chronic, inflammatory, recurring skin disease that affects 2-3% of the population. Psoriasis can start at any age, and is most often found in adults.
Juvenile plantar dermatosis
a disease characterized by localized damage to the feet. JPD usually occurs in children between the ages of 3 and 14 who are prone to atopy or have atopic dermatitis
Skin Conditions in Newborns: Causes, Symptoms, and Care Tips
Skin conditions like rashes, eczema, and cradle cap are common in newborns. Proper skin care is essential for managing and preventing these issues. Learn how to care for your baby’s delicate skin and address common skin conditions effectively.




