Epidermoid Cysts: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

- Epidermoid cysts are more common in adults, twice as often in men than in women
- It is more common in young or middle-aged people
- Certain genetic disorders can lead to the formation of multiple cysts (Gardner, basal cell nevi syndromes)
- The main reason for the formation of epidermoid cysts is the closure of the unit of the hair and sebaceous gland
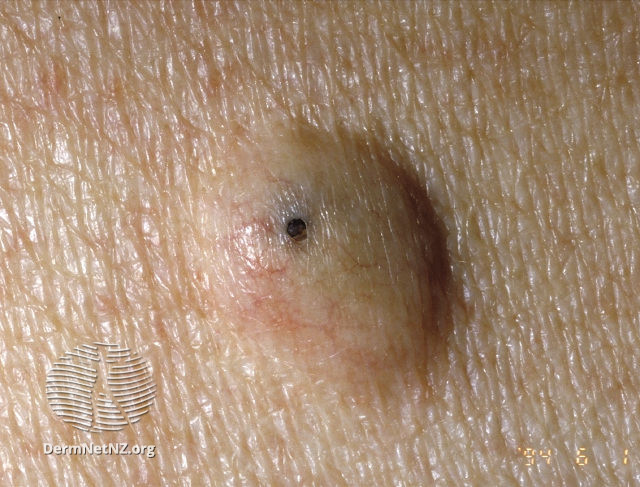
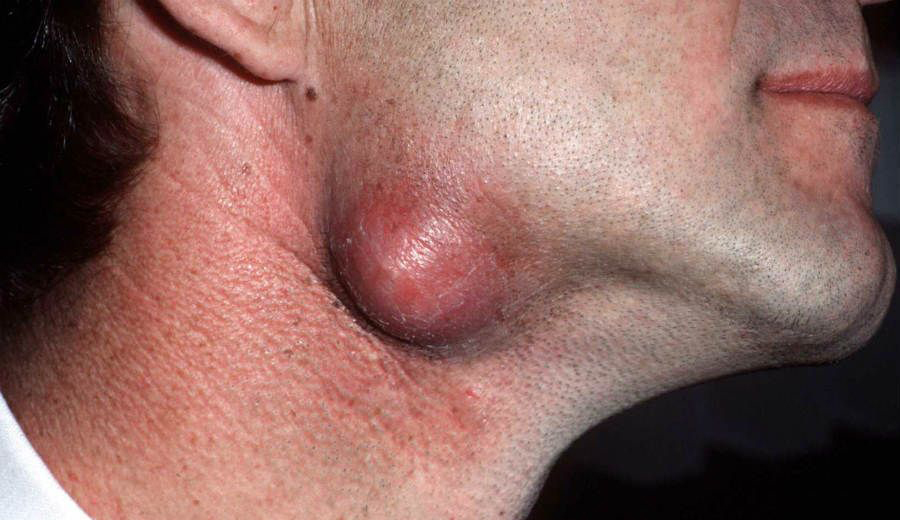
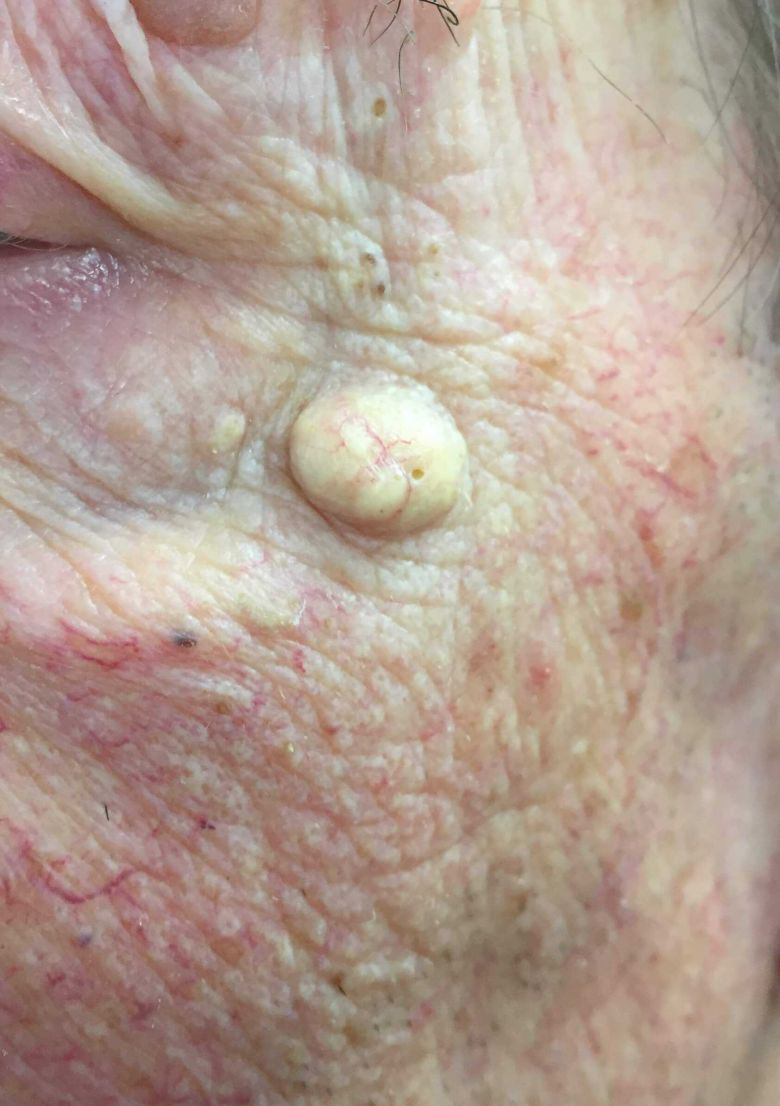
An epidermoid cyst is characterized by:
- a firm, flesh-colored or yellowish round papule (palpable bump on the skin) or nodule that is attached to the surface of the skin but usually moves in deeper layers
- diameter 1-3 cm
- the central point is visible
- inside the cyst, there is an accumulation of secretions with an unpleasant smell and a creamy consistency
- localization: more often in the central part of the body (chest, shoulders) and on the face, but can appear anywhere. Occurs in the vulva and scrotum
The patient’s examination and survey data are usually sufficient to establish the diagnosis. In rare cases, a skin biopsy or ultrasound examination of the skin mass may be performed.
Treatment
Most small, uncomplicated cysts do not require treatment.
In other cases, the main method of treatment is complete surgical removal of the formation. In this way, the chance of cyst formation again is reduced. An examination of the removed formation is also required in order to rule out a possibly started malignant process.
If the cyst is infected, antibiotic treatment is prescribed first, then the cyst contents are removed.
Prognosis
Epidermoid cysts are usually benign, slow growing and often resolve spontaneously. However, in rare cases, malignancy of the cyst may also occur.


Infectious mollusc
Infectious molluscMolluscum cont agiosum (Latin: Molluscum contagiosum) - A contagious viral disease characterised by shiny...
Flat lichen
Flat lichenLupus plan us/ruber: An inflammatory disease of the skin and/or mucous membranes of unknown origin, characterised by...
Folliculitis
FolliculitisFolliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicle. This is a common benign skin lesion. More severe forms may occur...





