Dishidrotic eczema

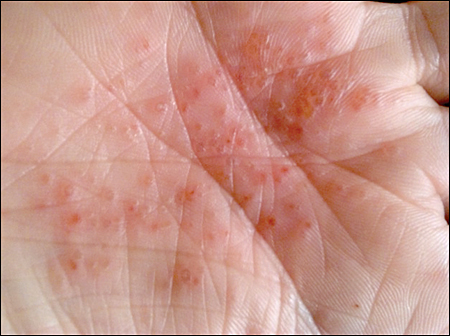
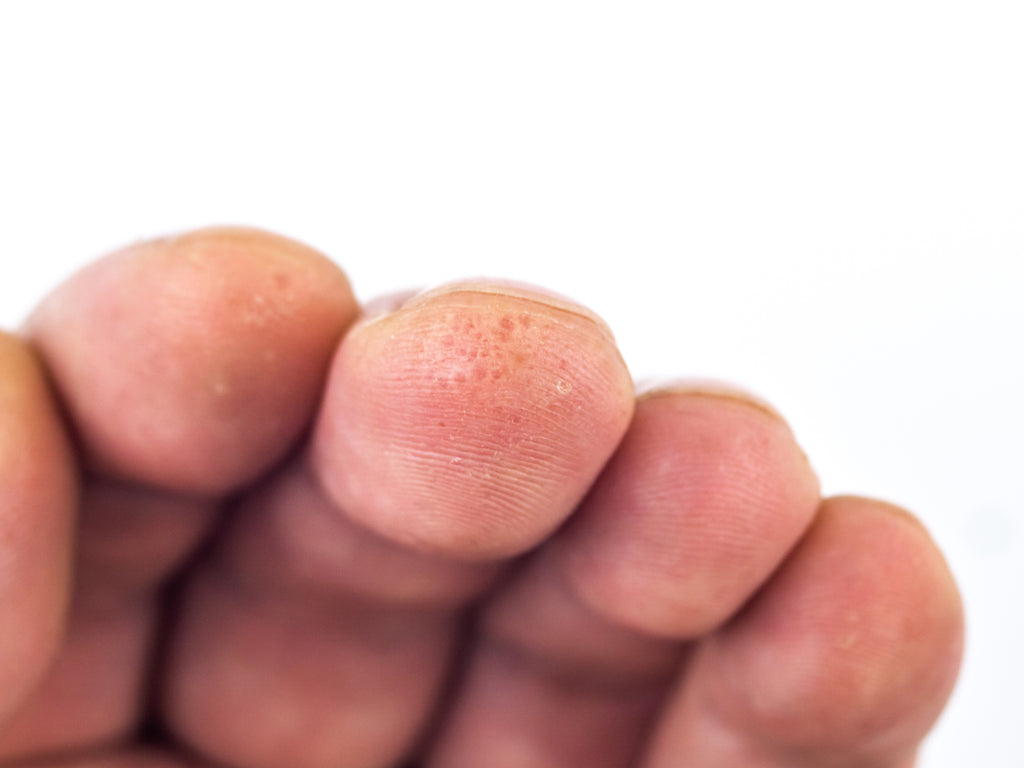
Dishidrotic eczema (syn. dishidrotic dermatitis, dishidrotic dermatitis, pompholyx) is a chronic, non-contagious inflammation of the skin affecting the hands and feet. The disease is more common in women and in patients with atopic dermatitis or contact allergies.
Clinical signs:
-
- characterised by an itchy rash with small subcutaneous vesicles
- a burning sensation may be felt at the site of the rash
- lesions on the skin of the hands, fingers, soles of the feet
- superficial wounds, skin fraying during healing
- the disease tends to recur
Risk factors:
-
- genetic predisposition
- increased sweating of the hands and feet
- humid environment, frequent contact with chemicals (e.g. hand washing, washing dishes or floors)
- sensitisation or allergy to environmental factors, most commonly nickel
- reaction to medicines
- emotional stress
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is based on characteristic clinical signs. If there is a suspicion that the rashes may be provoked by environmental substances or allergies, an allergen patch test is carried out and a doctor consultation with an allergist/clinical immunologist may be recommended.
If the diagnosis is in doubt, a biopsy of a skin graft may be performed.
Treatment
-
- Avoidance of factors that provoke rashes is recommended (humid environment, allergic substances if found)
- your doctor will assess the extent of the disease and choose topical preparations or a combination of oral medicines.
- phototherapy treatments may be prescribed
Prophylaxis to prevent recurrence of rashes:
-
- wearing cotton gloves and rubber gloves when working with wet hands
- reducing profuse sweating (proper choice of footwear made of natural materials, cotton socks, antiperspirants, botulinum injections, etc.)
- hand and foot creams to ensure good skin barrier properties

Psoriasis
A common, chronic, inflammatory, recurring skin disease that affects 2-3% of the population. Psoriasis can start at any age, and is most often found in adults.
Juvenile plantar dermatosis
a disease characterized by localized damage to the feet. JPD usually occurs in children between the ages of 3 and 14 who are prone to atopy or have atopic dermatitis
Skin Conditions in Newborns: Causes, Symptoms, and Care Tips
Skin conditions like rashes, eczema, and cradle cap are common in newborns. Proper skin care is essential for managing and preventing these issues. Learn how to care for your baby’s delicate skin and address common skin conditions effectively.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškės g. 99, Vilnius
+370 671 33323
[email protected]




