Dishidrotic eczema

Dishidrotic eczema (syn. dishidrotic dermatitis, dishidrotic dermatitis, pompholyx) is a chronic, non-contagious inflammation of the skin affecting the hands and feet. The disease is more common in women and in patients with atopic dermatitis or contact allergies.
Clinical signs:
-
- characterised by an itchy rash with small subcutaneous vesicles
- a burning sensation may be felt at the site of the rash
- lesions on the skin of the hands, fingers, soles of the feet
- superficial wounds, skin fraying during healing
- the disease tends to recur
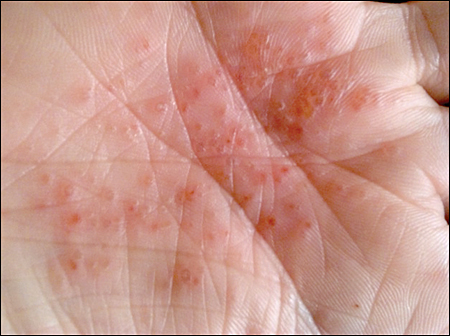
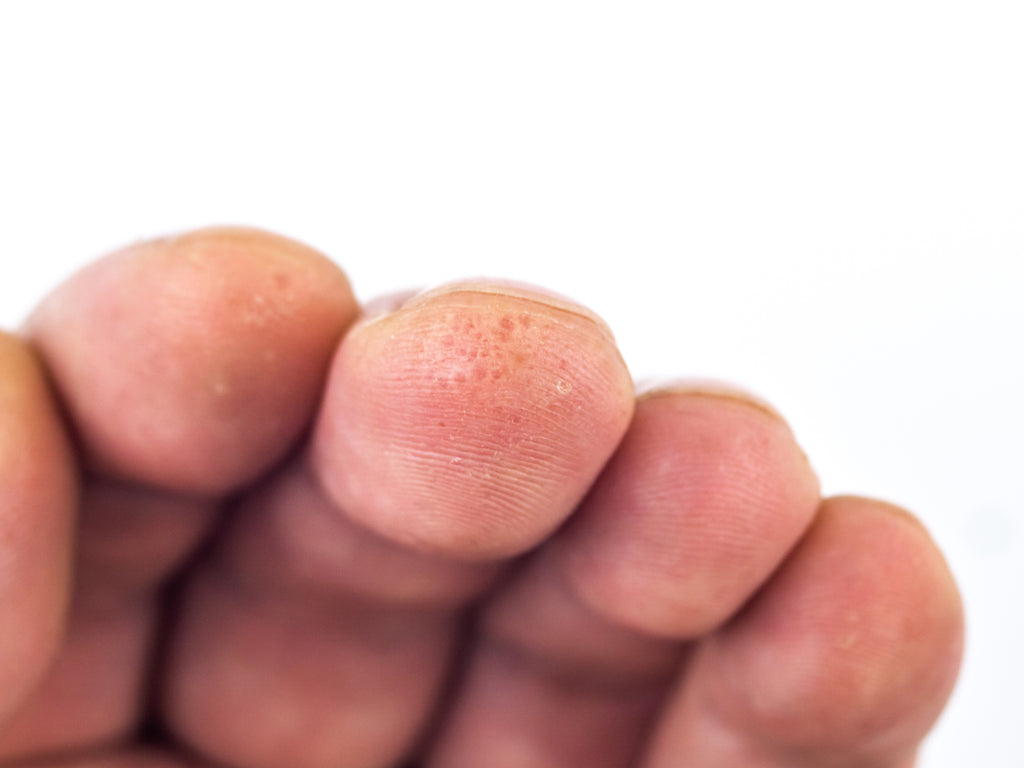
Risk factors:
-
- genetic predisposition
- increased sweating of the hands and feet
- humid environment, frequent contact with chemicals (e.g. hand washing, washing dishes or floors)
- sensitisation or allergy to environmental factors, most commonly nickel
- reaction to medicines
- emotional stress
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is based on characteristic clinical signs. If there is a suspicion that the rashes may be provoked by environmental substances or allergies, an allergen patch test is carried out and a doctor consultation with an allergist/clinical immunologist may be recommended.
If the diagnosis is in doubt, a biopsy of a skin graft may be performed.
Treatment
-
- Avoidance of factors that provoke rashes is recommended (humid environment, allergic substances if found)
- your doctor will assess the extent of the disease and choose topical preparations or a combination of oral medicines.
- phototherapy treatments may be prescribed
Prophylaxis to prevent recurrence of rashes:
-
- wearing cotton gloves and rubber gloves when working with wet hands
- reducing profuse sweating (proper choice of footwear made of natural materials, cotton socks, antiperspirants, botulinum injections, etc.)
- hand and foot creams to ensure good skin barrier properties

Paraneoplastic dermatological manifestation of gastrointestinal malignancies
rare disorders resulting from the immune system’s response to a cancerous process (neoplasia) in the body. Gastrointestinal neoplasms more often cause paraneoplastic syndromes affecting the skin.
Nail psoriasis
Psoriasis is a form of chronic systemic inflammatory autoimmune disease that mostly affects fingernails and toenails.
Lyme disease
It is contracted when a blood-sucking tick injects intestinal contents containing bacteria into a wound. Untreated Lyme disease can damage not only the skin, but also the internal organs, joints and nervous system.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškės g. 99, Vilnius
+370 671 33323
[email protected]




