Contact Dermatitis
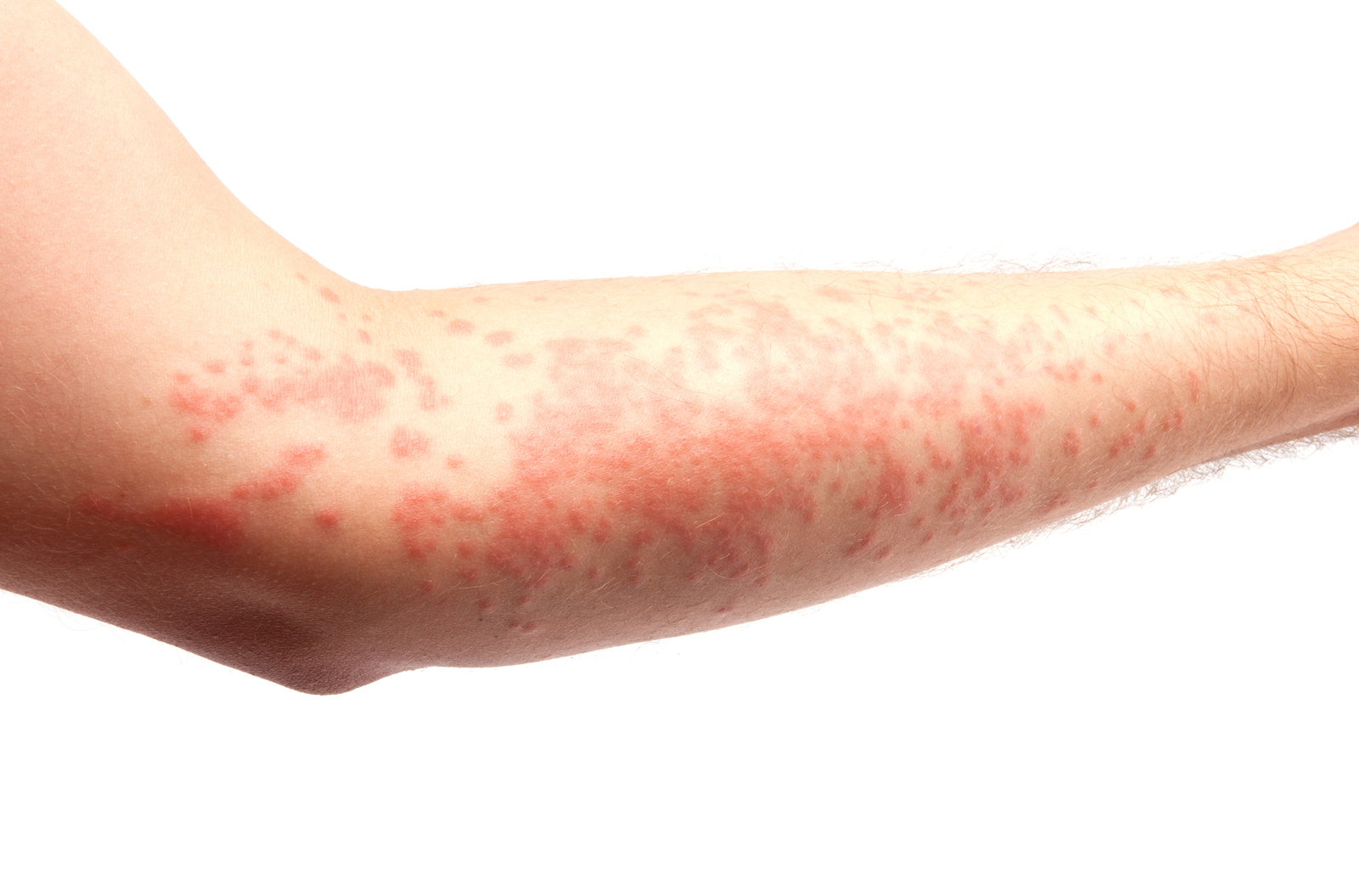
Symptoms:
- Redness, swelling;
- Itching
- Dandruff
A more difficult course:
- Blisters, vesicles, nodules
- Pain
- Cracks
- Urination
- Scabies
- Skin thickening
1.
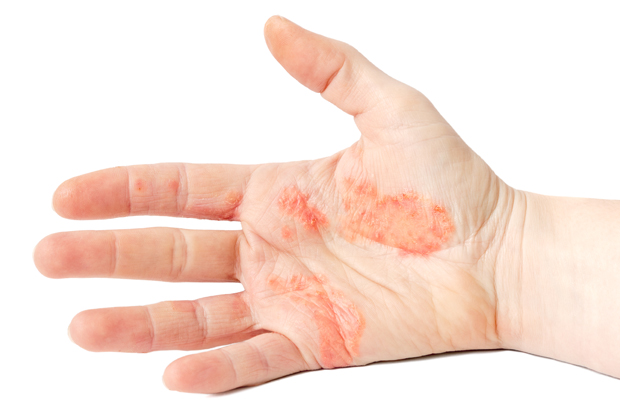
Allergic contact dermatitis
– When your skin comes into direct contact with an allergen, your immune system is activated and rashes appear as soon as 12 to 48 hours after the first contact with the substance, but also after a week or a month using the same substance.
Common allergens: metals (nickel, chromium, cobalt), fragrances, preservatives (formaldehyde, parabens, methylchloroisothiazolines), Peruvian balsam, latex, etc.
2.
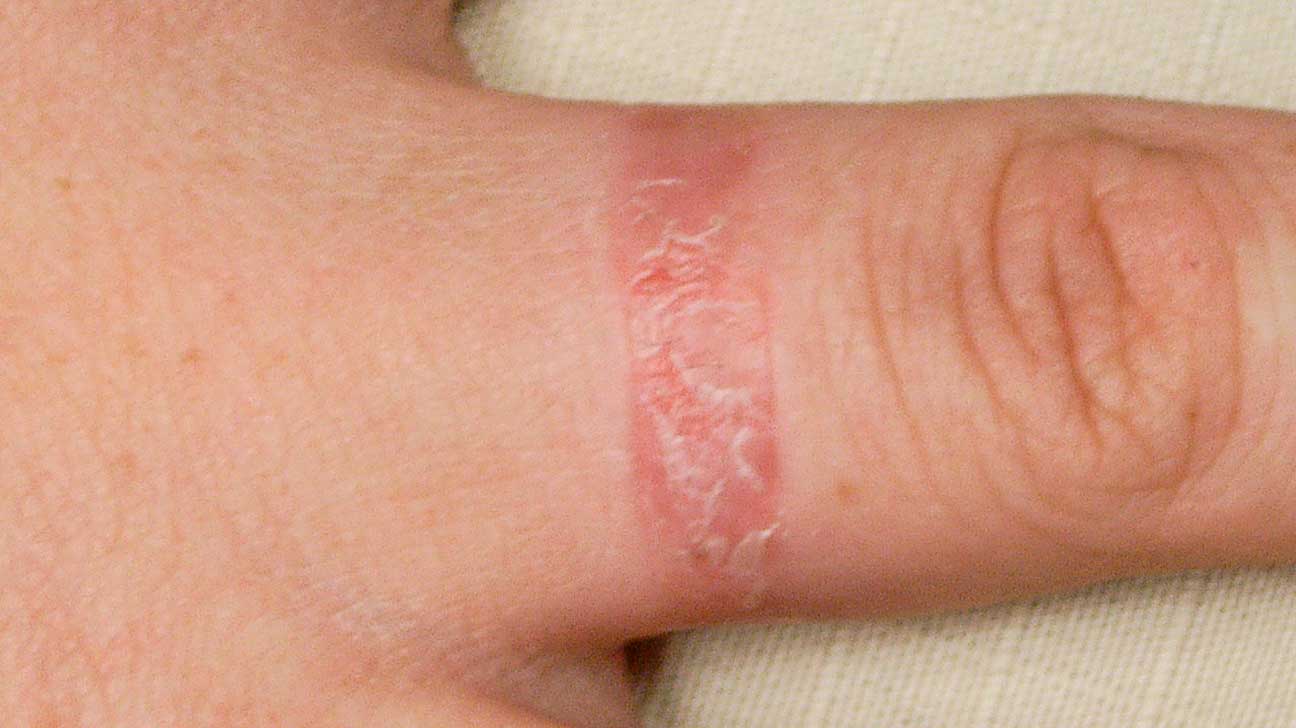
Irritant contact dermatitis
– A physical, mechanical or chemical breach of the skin barrier caused by direct contact of the skin with an irritant (irritant).
Common irritants: products used every day (detergents, softeners, laundry detergents, cleaning products).
The diagnosis of contact dermatitis is based on your medical history (questionnaire) and physical examination (examination, palpation). Specialised tests – the allergen patch test – are only performed when the diagnosis is unclear or the treatment is ineffective, and are prescribed by a dermatovenerologist or allergist.
How can you prevent contact dermatitis?Preventive measures
- Avoid contact with substances that cause dermatitis;
- Wear rubber gloves when doing household chores and cotton gloves underneath;
- Apply nourishing and barrier (oily) skin emollients (creams, ointments) 2-3 times a day and after each hand wash.
First aid for dermatitis:
- Do not touch substances that may have caused dermatitis;
- Wash surfaces and areas of the body touched by the allergen or irritant with water;
- Apply nourishing and top barrier emollients (creams, ointments) 2-3 times a day and after each hand wash;
Interesting and important to know:
- Contact dermatitis is not hereditary and not contagious;
- 20% people in the world have been diagnosed with contact dermatitis at least once;
- Irritant dermatitis accounts for ~80% of all dermatitis cases of contact dermatitis;
- The disease is more common in women than in men, due to their more frequent household chores and occupation;
- See your doctor if the rash does not go away within 2 weeks or gets worse;

Acute Urticaria: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Acute urticaria is a skin condition characterized by red, itchy hives and swelling, often caused by an allergic reaction. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing future flare-ups through medication and lifestyle adjustments.
Geographic Tongue: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Geographic tongue is a benign condition that causes smooth, red patches on the tongue, surrounded by white lines. Although usually harmless, it can cause discomfort, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving oral health.
Epidermoid Cysts: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Epidermoid cysts are firm, flesh-colored bumps beneath the skin caused by trapped skin cells. They often have a visible central point and can be treated with minor surgery if needed, though most are harmless.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškės g. 99, Vilnius
+370 670 70 822
[email protected]




