Candidiasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Yeast Infections

- The most common causative agents: C. albicans (80%), C. parapsilosis, C. tropicalis
- Small amounts can be found on the skin, mucous membranes and in the digestive tract
- Causes diseases only when favorable conditions occur, when the immune system is weakened
Risk factors
- humid, warm environment
- profuse sweating
- weakened immune system
- hormonal disorders, metabolic diseases
- some medicines (antibiotics)
Classification
- Skin:
-
- Yeast Diaper Rash
- Yeast Skin Folds Rash
- Candidal intertrigo (between fingers)
-
- Oral mucous membranes

Yeast Diaper Rash
Candidiasis is a common disease in newborns, but it can also affect adults. Rashes appear in the diaper area.
- Characterised by: redness, scaling, papules (palpable bumps on the skin), blisters, erosions (small damage to the surface layer of the skin)
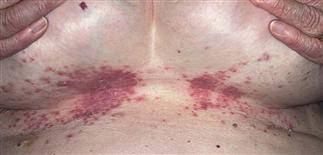
Yeast Skin Folds Rash
Candidal infection occurs in places where natural body folds are formed: groin, armpits, under the breasts, around the navel, between the buttocks.
- Characterised by: redness, scaling, papules, erosions, blisters, urination. Also itching/stinging of the skin
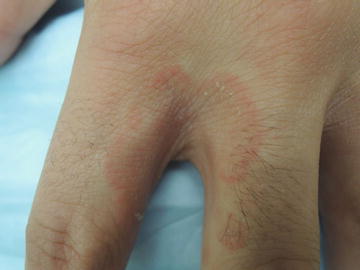
Candidal intertrigo (between fingers)
Candidiasis infection occurs more often in the intertoes of the hands, less often in the toes.
- Characterised by: redness, scaling, erosions, hardening of the skin
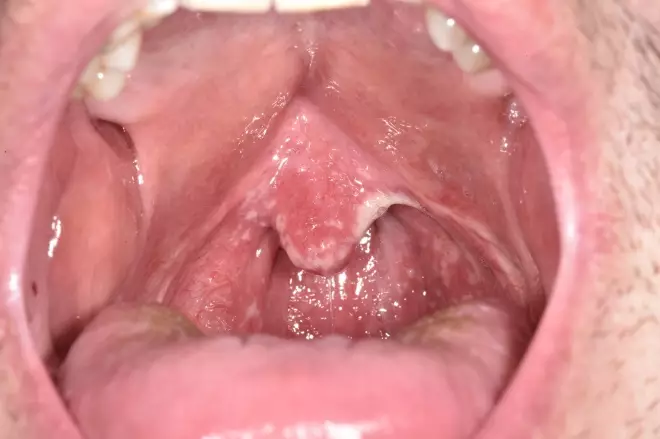
Oral mucous membranes manifestation of candidiasis:
- Redness, pain when eating or swallowing, loss of taste, cracked and reddened corners of the lips, feeling of sensation in the mouth, white spots on the inside of the cheeks, on the tongue, in the upper part of the oral cavity, in the throat
Most of the time, data from the anamnesis and the clinic are sufficient to establish the diagnosis.
If the data from the anamnesis and the clinic are insufficient, sometimes laboratory tests may also be necessary (examination material: skin scales, scrapings of the focus of damage, nails):
- Microscopic examination of the test material in search of parts of the fungus
- Microbiological studies
Treatment
During the consultation, the treatment is selected for each patient individually according to the form of disease manifestation, general condition.
Local treatment with topical antifungal drugs is usually prescribed. If this treatment is ineffective, the disease is widespread and tends to recur, then treatment with oral antifungal drugs may be prescribed.
Prevention
In order to prevent skin candidiasis infection, it is important to eliminate or reduce risk factors:
- do not wear tight, rubbing clothes
- change diet, lose weight
- control blood glucose levels
- avoid constant skin moisture (drying substances can be used, e.g. talcum powder)
In order to prevent oral candidiasis or recurrent episodes, it is advisable to:
- follow oral hygiene
- after using an inhaler with glucocorticoids (hormones), thoroughly clean the oral cavity

Psoriasis
A common, chronic, inflammatory, recurring skin disease that affects 2-3% of the population. Psoriasis can start at any age, and is most often found in adults.
Juvenile plantar dermatosis
a disease characterized by localized damage to the feet. JPD usually occurs in children between the ages of 3 and 14 who are prone to atopy or have atopic dermatitis
Skin Conditions in Newborns: Causes, Symptoms, and Care Tips
Skin conditions like rashes, eczema, and cradle cap are common in newborns. Proper skin care is essential for managing and preventing these issues. Learn how to care for your baby’s delicate skin and address common skin conditions effectively.




