Atopic Dermatitis in Children: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment

- Worldwide, 5-20% of children suffer from atopic dermatitis
- In the majority of sufferers, the symptoms disappear by adulthood, although they may recur later
- The disease is characteristic for children with other allergic diseases
- The manifestation of atopic dermatitis is strongly influenced by heredity
Risk factors
The occurrence of atopic dermatitis can be provoked by certain factors:
- Įvarious allergens: food, environmental (house dust, dust mites, pollen and others), contact allergens (nickel, chromium and others)
- Skin drynesss
- Skin infections
- Irritants (wool, synthetics, washing powder, building materials and others)
- Bad climate, frequent sweating
- Psychological stress
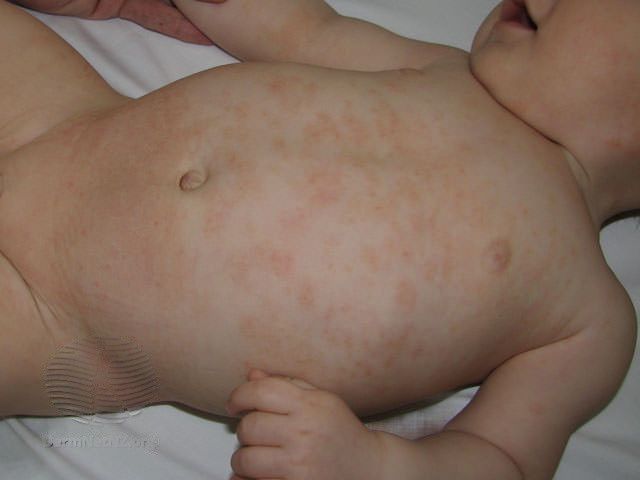
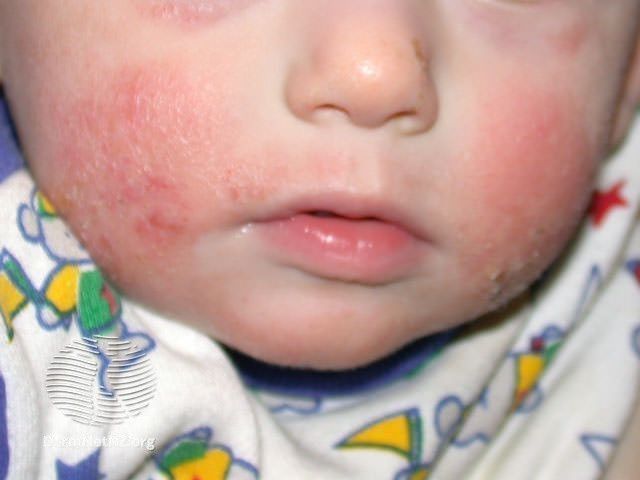
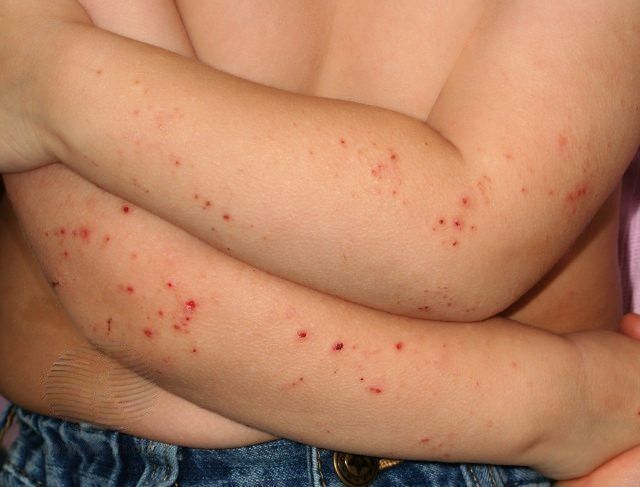
Atopic dermatitis in babies and young children (up to 4 years) manifests itself a little differently than in adults:
- red, palpable bumps on the skin of a limited area of various sizes, blisters are characteristic
- redness of the skin, urination, scabs prevail
- characterized by severe itching
- sleep and mood problems can contribute
- localization: face, neck, chest, hairy part of the head, extensor (external), and less often flexor (internal) surfaces of the limbs
The patient’s survey and examination data are usually sufficient to establish the diagnosis. Atopic dermatitis is often characteristic of children with allergic diseases, so additional tests may be performed:
- Blood test to determine the concentration of IgE
- Skin allergy samples
- Skin biopsy (in rare cases, to confirm the diagnosis)
Treatment
During the consultation, the treatment is selected for each patient individually, taking into account the patient’s general condition, age, severity of the disease. For treatment can be used:
- Moisturizing creams, emollients
- Hormones (glucocorticoids) and other ointments
- Antihistamines
- Antibiotic ointments or oral medications (in case of secondary bacterial skin infection)
- Phototherapy
- Medicines that alter the immune system
Other general measures are also important:
- Cut your child’s nails short to prevent scratching and subsequent secondary bacterial skin infection
- Use special hygiene products for sensitive skin
- Avoid irritants, allergens

Athlete’s Foot: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment
Foot fungus or Athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) is the most common fungal skin infection that affects the soles, between the toes and the edges of the feet…
Scabies
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by mites, leading to intense itching and a rash. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent spreading. Learn how to identify, treat, and prevent scabies for healthy skin.
Polymorphic light rash (sun allergy)
Polymorphic light eruption, also known as sun allergy, is a skin condition triggered by sun exposure, leading to itchy, red rashes. This seasonal allergy often requires protective measures and specific treatments to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.




