Adult acne.
Is acne just a teenage disease?
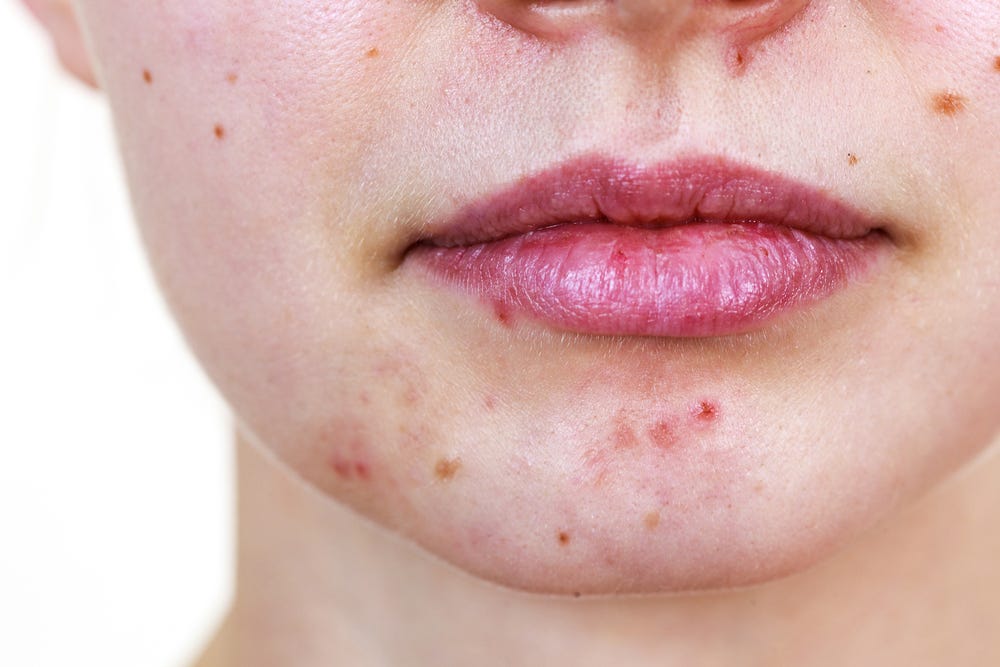
There are three main subtypes of adult acne:
- Persistent acne: the most common type, found in 70-80% of cases, where acne appears in adolescence and continues into later life.
- Late-onset acne: affects 20-40% of women, with acne first appearing at the age of 25 or later.
- Recurrent acne: when acne appears in adolescence, goes away for a while and then flares up again at an older age. This subtype is the least described and thought to be the rarest.
Unlike teenage acne, adult acne has a “U” shape – on the lower jaw, chin and neck. Skin oiliness is less frequent, and sometimes there may be fewer (or no) comedones.
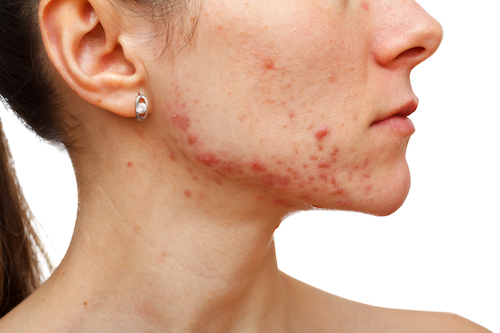
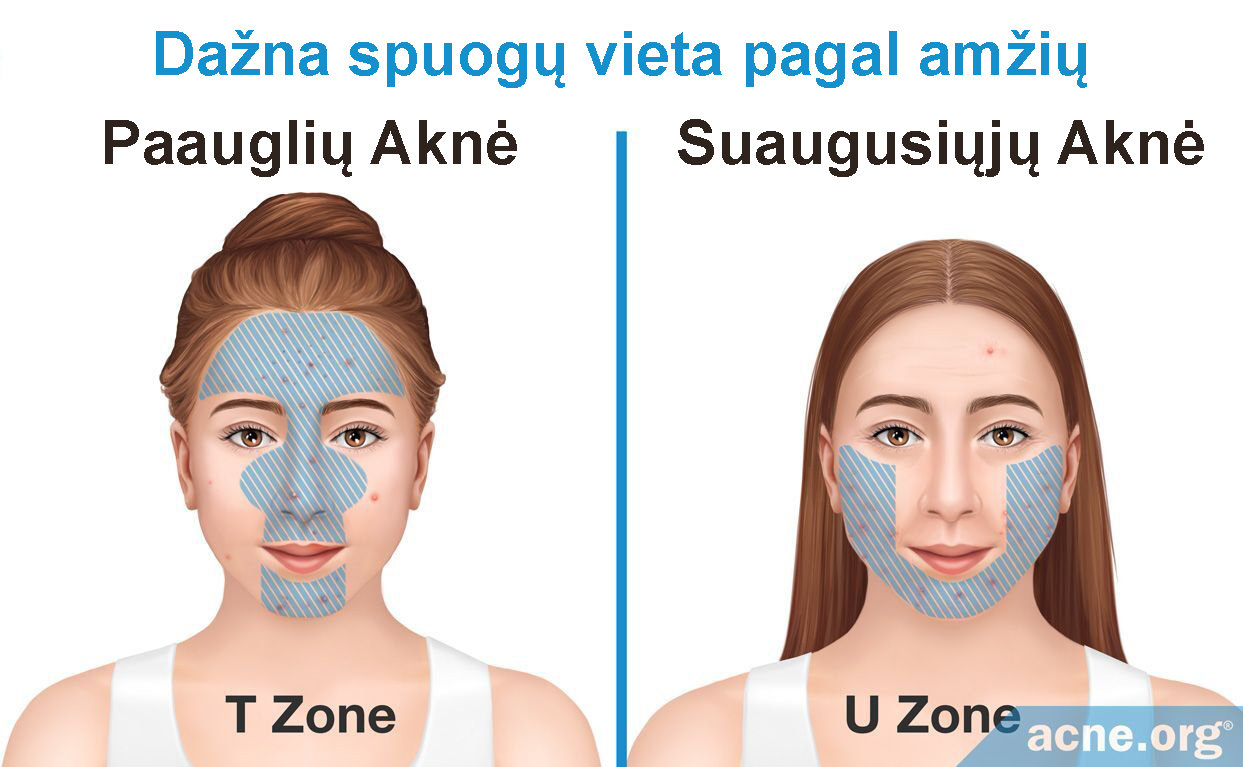
-
- Genetic predisposition
- Diet
- Tobacco use
- Chronic stress
- Cosmetics used
- Medicines
Regardless of the severity of acne, a good daily skincare routine is essential:
-
-
- Non-comedogenic and gentle cleanser (pH 4-6)
- Moisturising cream
- Sun protection
-
There is also a growing body of evidence on the importance of the skin barrier in balancing the skin microbiome.
It is therefore recommended to use moisturising creams to help rebuild the skin barrier and to avoid aggressive, irritating and drying substances.

Pityriasis rosea
An acute, self-limiting, exanthematic skin disease that manifests as itchy, somewhat inflammatory, scaly rashes, usually on the torso, chest, and upper limbs.
Peeling skin syndrome
Peeling skin syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by constant peeling of the skin. The disease appears from birth or in the first year of life
lasts a lifetime
Mycosis Fungoides
The most common primary skin T-cell lymphoma (cancer of the blood). Mycosis Fungoides is characterized by three main stages, several of which may exist at the same time
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškės g. 99, Vilnius
+370 670 70 822
[email protected]




